Rapid Casting
★ Rapid Investment Casting 10-100 pcs in 7-15 days
★ Rapid Gravity Casting 50-500 pcs in 10-20 days
Rapid Casting Services
ProtoWe is a leading China Rapid Casting manufacturer who provides Rapid Investment Casting & Rapid Gravity Casting services to global clients. Our customers would benefit from our excellent rapid casting solutions by getting high quality castings within 2 weeks without paying high mold costs. Nornally, we could save clients 40%-60% cost than CNC machining or die casting processes and approximate 50% cost than western competitors.
Rapid Investment Casting
Rapid Gravity Casting
Rapid Casting Solutions
ProtoWe provides 2 solutions for a rapid casting project: Rapid Investment Casting & Rapid Gravity Casting. The 2 solutions have different features.
Rapid Investment Casting best for 10-100 units /7-15 days or 100-500 units /15-25 days. 70% cost saved than CNC machining.
Rapid Gravity Casting best for 100-500 units /10-20 days or 500-1,000 units /20-25 days. 50% cost saved than CNC machining.
Advantages of Investment Casting
- Can achieve very thin-walled parts with complex shapes
- Very accurate, even net shape with precise dimensions
- Excellent surface finishes save machining and finishing
- Ferrous and nonferrous metals, as well as duplex alloys can be used
- Tooling cost could be negligible over repeat runs
Rapid Investment Casting
Advantages of Gravity Casting
- Tight tolerances allow for excellent accuracy in finished parts
- Much smoother surface finish than sand casting
- Mechanical properties are superior to sand casting, including tensile strength
- Insertable sand core parts can be pre-formed and used to create reverse draft interior pockets
- Tooling cost saved much than a die casting mold
Rapid Gravity Casting
Materials of Investment Casting
There are very broad of materials to be used for investment casting. It’s included Ferrous and nonferrous metals, as well as duplex alloys. Below materials are commonly used in ProtoWe.
- Stainless Steel
- Carbon Steel
- Low Alloy Steel
- Aluminum Alloy
- Copper Alloy
- Zinc Alloy
- Cast Iron
Materials of Gravity Casting
The materials used to gravity is limited to low melting nonferrous metals. At ProtoWe, we often use cast below alloys.
- Aluminum Alloy
- Zinc Alloy
- Copper Alloy
Surface Finishings for
Investment Castings & Gravity Castings
Investment casting and gravity casting have similar surface finishes. These processes/treatments include :
- Magnetic Abrasive Polishing
- Electro Polishing
- Vibratory Finishing
- Passivation
- Sand Blasting
- Shot Blasting
- Clear Chemical Film Coating
- Zinc Plating
- Barrel Tumbling
- Hand Polishing
- Powder Coating
- Electroless Nickel Coating
- Alochroming /Anodising
- Painting
Sand Blasting Effect
Recommended Surface Finishes for Rapid Casting
Although there are diversified surface finishes for both investment castings and gravity castings that all achieve a good surface effect. While from the view of cost and practicability, there are still some important surface finishes to be recommended for rapid casting by ProtoWe.
- Hand Polishing (★ ★ ★ )
- Magnetic Abrasive Polishing (★ ★ ★ ★ ★ )
- Sand Blasting (★ ★ ★ ★ ★ )
- Shot Blasting (★ ★ ★ ★ )
- Electro Polishing (★ ★ ★ )
Magnetic Abrasive Polishing Effect
Rapid Investment Castings
( remark: below investment casting parts with surface finishes )
Rapid Gravity Castings
( remark: below gravity casting parts without surface finishes )
What's Investment Casting
Investment casting, also known as lost wax casting, is a precision casting process using lost wax method to make precision components in any cast alloys. Investment casting process starts from creating a wax pattern (same dimensions as finished components) by injecting wax into a vacuum casting (silicone) mold. Then dipping the tree assembly into refractory slurry to form a ceramic shell. Finally pouring melton metal into the shell by sprue gate then cooling for solid casting blanks.
Investment Casting
What's Gravity Casting
Gravity casting, also called as gravity die casting, is a precision casting process that molten metal is directly poured into a low-cost steel mold to make precision castings in nonferrous metal alloys. A gravity casting mold is normally made of low-cost mild steel like 1.1730 (C45,45#) with simple mold structure. One or more sand cores will be used in a gravity casting mold if the component has undercuts.
Rapid Molding
What's the processes of Investment Casting?
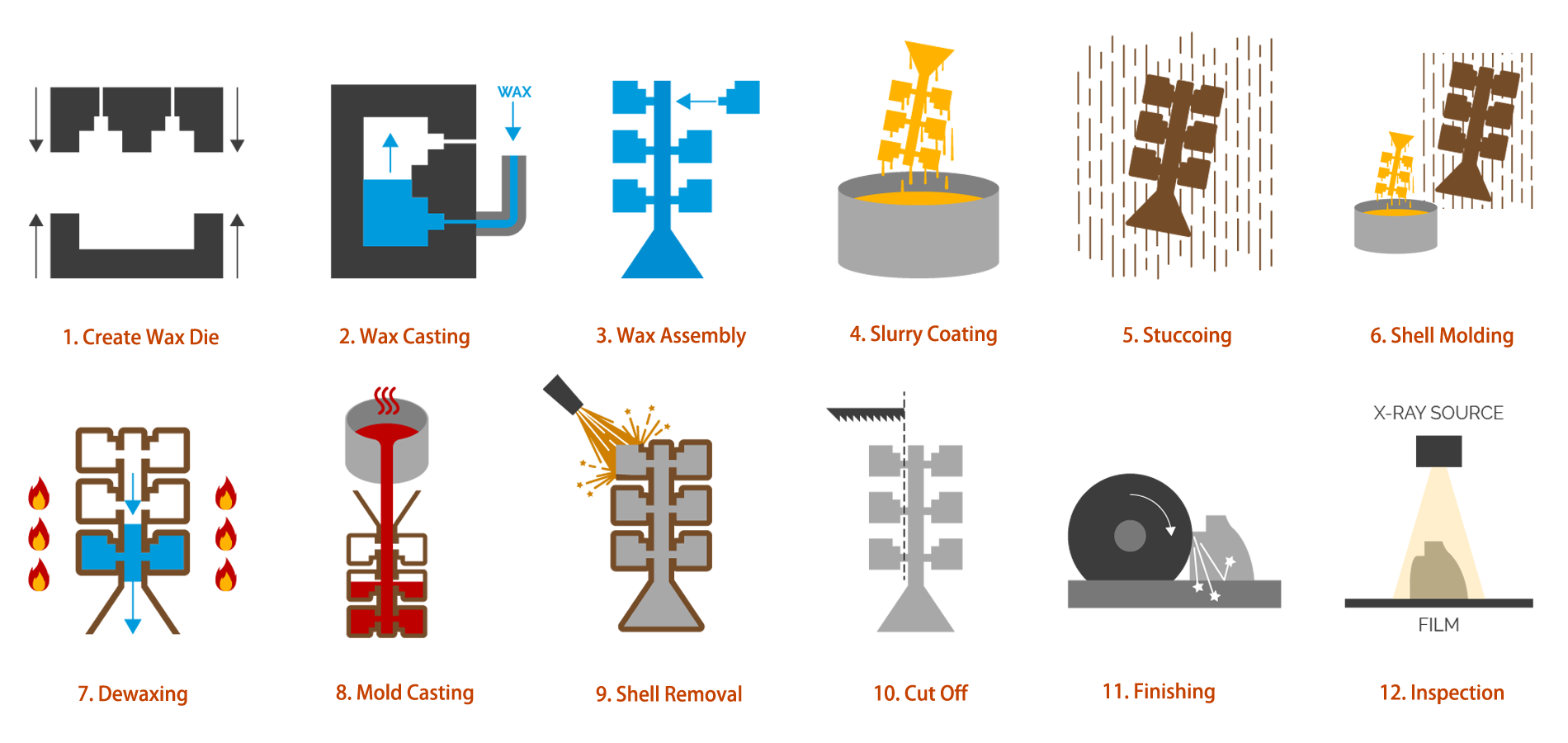
Investment casting, using the lost wax technique, is one of the earliest known casting processes, and its application in the creation of jewelry and sculptures dates back several thousand years. With origins in ancient Mesopotamia and Egypt, its commercial existence really started during World War II, when the machine tool industry was overburdened by military needs. Investment casting is a technique that may be used to create complicated parts and components. There are various distinct phases involved in designing and fabricating the appropriate workpieces. It is so called because the workpieces are made around a shelled casting, which is then removed once the workpieces have been poured and hardened in the mold.
Step-1: Create Wax Dies
The first step in the process is to create a model (called pattern) by SLA 3D printing, then use the printed pattern to reverse casting a silicone mold which called a wax die.
Step-2: Wax Casting
Injection liquid wax into dies then rotate and air cool the dies to get hollow solid wax patterns.
Step-3: Wax Assembly
Next, the wax patterns are assembled onto runners and into a finished tree which is ready to be dipped.
Step-4: Slurry Coating
The assembly is then dipped into a high-grade ceramic slurry to coat a ceramic shell around the wax tree.
Step-5: Stuccoing
After the slurry coating is done, particles of sand are dropped onto the surface of the wet tree assembly. This helps to thicken and strengthen the layer of coating on the wax assembly surface.
Step-6: Shell Molding
Repeat steps 4 and 5 until the mold is thick enough to handle casting stresses. The molding must fully dry before it can be used.
Step-7: Dewaxing
The wax inside the newly built shell is now removed. Dewaxing is done using a steam-dewaxing autoclave or flash fire furnace.
Step-8: Mold Coating
Now the desired molten metal is poured into the pre-heated mold cavity.
Step-9: Shell Removal
The shell material is then removed through processes hammer knockout, vibration, and steel grit blasting.
Step-10: Cut Off
The finished parts are then cut free from the gating and runner system.
Step-11: Finishing
Various finishing techniques are then employed including grinding, sand blasting and coating to achieve the final surface needed.
Step-12: Inspection
Once the finishing operations are done, the parts are inspected for surface and sub-surface defects. Visual and fluorescent penetrant inspection is done for surfaces and X-ray is employed for sub-surface defect identification.
Investment Casting VS Sand Casting VS Gravity Casting VS Die Casting
There are many ways to get a casting part: investment casting, sand casting, gravity casting and die casting. Each method has its advantages and disadvantages. Therefor it’s hard to say which is better, just for different application. Here ProtoWe gives the ultimate casting process comparison chart.
| Process | Investment Casting | Sand Casting | Gravity Casting | Die Casting |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Metals Cast | Nearly all ferrous and non-ferrous alloys | Wide range of ferrous and non-ferrous alloys | Nonferrous alloys (Al, Zn, Mg, certain Cu), some Fe | Nonferrous alloys only (Al, Zn, Cu, Mg, Sn, Pb) |
| Complexity of Shape | 4 (Greatest) | 3 | 2 | 1 (Least) |
| Casting Weight | 30g-113kg | 60g to Tons | 30g-113kg | 30g-18kg |
| Min. Section Thickness | 0.5-2mm | 3-6mm | 1.5-6mm | 0.6-2mm |
| Linear Dimensional Tolerances | Under 25mm: +/-0.1mm. Over 25mm add +/- 0.05mm per 25mm | Common +/- 0.4mm-6mm. Add +/- 0.4mm-6mm across parting plane | Under 25mm: +/-0.25mm. Over 25mm add +/- 0.05 mm per 25mm Add +/-0.4-1.5mm across parting plane | Common +/-0.04-0.13mm. Add +/-0.02-0.13mm across parting plane |
| Surface Finish (Ra/um) | 1.6-3.2um | 3.8-12.7um | 3.8-8.9um | 0.8-1.6um |
| Tooling Costs | Low-to-Moderate | Low | Moderate | High |
| Optimum Lot Size | Small-to-Medium depending on degree of process mechanization | Small-to-large depending on degree of process mechanization | Medium | Large |
| Draft Required | None | 1-5 degrees | 2-5 degrees | 1/2 to 2 degrees |
| Advantages | No Parting Plane. Accommodates nearly all metals. Near-net-shape castings require minimal machining. | Sand mold cost is low | Mold life of 100,000 cycles or more depending upon pouring temperature of metal and upon casting specs. Both metal and sand cores are used. | Mold life from 30,000 cycles depending upon pouring temperature of metal and upon casting specs. Near-net-shape castings require minimal machining. |
| Disadvantages | Mold is not reusable. Mold materials not reusable. Process is labor and energy intensive | Mold is not reusable. | Some shapes cannot be casted. | Sealing may be required to achieve pressure or leak tight castings. Metal cores only. Sand cores cannot be used. |
Also interested in our Rapid Tooling services? Just follow this link Rapid Tooling.
